Abrocitinib: A Revolutionary Treatment for Netherton Syndrome?
A recent case study has highlighted the potential of abrocitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, in managing Netherton Syndrome, a rare condition that manifests with debilitating skin symptoms and increased risk for severe infections. The case involved a 29-year-old female patient who, after six months of treatment, exhibited significant improvements in various disease symptoms, although not without limitations.
Understanding Netherton Syndrome
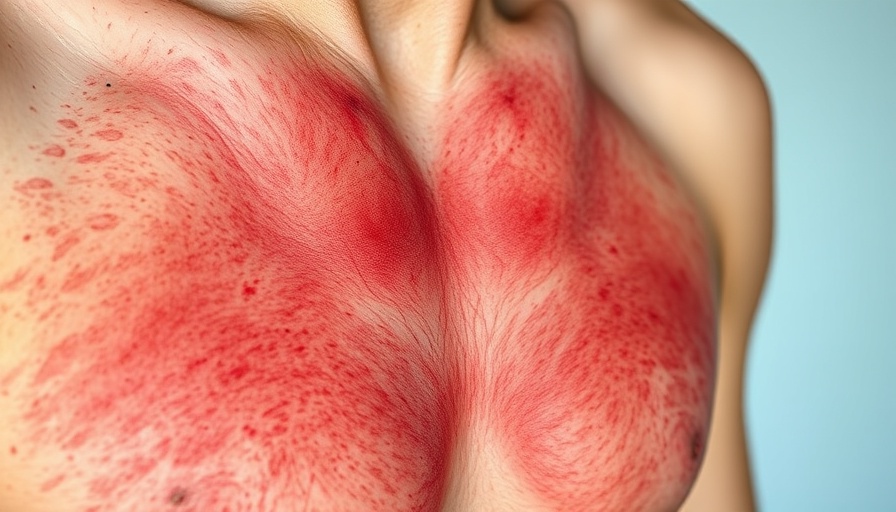
Netherton Syndrome is caused by mutations in the SPINK5 gene, which leads to a dysfunctional skin barrier and an array of immune system challenges. The syndrome presents itself through symptoms such as erythroderma and desquamation from birth, which can lead to severe complications later in life. Patients often experience crusted lesions, hair abnormalities, and heightened susceptibility to infections including HPV and certain skin cancers.
The Case Study Breakdown: Improvements Noted
The patient underwent treatment with abrocitinib after various conventional therapies failed to provide relief. Within six months, her clinical scores for disease severity improved significantly, with reductions in body surface area affected (BSA), Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), and Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) scores. This indicates a noteworthy advancement in managing her condition, showcasing abrocitinib’s potential as a therapeutic option.
Limitations: The Bamboo Hair Phenotype
Despite these improvements, the treatment did not restore the characteristic bamboo-like hair phenotype often associated with Netherton Syndrome. This limitation underscores the complexity of treating genetic conditions where a complete cure remains elusive, reflecting that management must be tailored to each patient's unique needs.
Next Steps in Research and Development
While the results from this case report are promising, more extensive clinical trials are necessary to validate abrocitinib’s efficacy and safety across a broader patient population. Current treatments, though varied, often do not yield satisfactory results in managing the symptoms or preventing complications of Netherton Syndrome.
Future Predictions: Opportunities in Treatment
As research progresses into JAK inhibitors and their application in dermatological diseases, there is hope that additional therapies could emerge, providing communities affected by rare conditions new avenues of treatment. Emphasis must remain on understanding individual patient responses to these therapies, as genetic factors can significantly influence efficacy.
What This Means for Patients
For patients or caregivers dealing with Netherton Syndrome, the insights from this case study could lead to proactive discussions with dermatologists about the potential of medication like abrocitinib. It represents a step forward in exploring therapies that could alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life, even if challenges remain.
Emotional and Human Interest: The Patient Perspective
The journey of this patient through various inadequate treatments to discovering potential relief could resonate deeply with many. Patients in similar circumstances often feel isolated and desperate for viable options. Abrocitinib’s promise might just offer a glimmer of hope and strength amid ongoing challenges.
Conclusion: Calling for Action
To the community of patients and healthcare providers, understanding new treatment options like abrocitinib is essential. Though still under research, discussing these findings with doctors can pave the way for pivotal changes in management strategies for this rare syndrome. As data emerges, staying informed will be critical for all those affected by this condition.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment